Start writing here...
Virtual Machine abstracts the hardware of our personal computers, such as CPU, disk drives, memory, NIC (Network Interface Card), etc., into many different execution environments as per our requirements, hence giving us a feeling that each execution environment is a single computer.
For example, VirtualBox. We can create a virtual machine for several reasons, all of which are fundamentally related to the ability to share the same basic hardware yet also support different execution environments, i.e., different operating systems simultaneously.
Methods to Install VirtualBox on our Debian-based Linux system
Here are three ways to download VirtualBox on a Debian-based system like Ubuntu. Each method offers different advantages, such as convenience or the ability to get the latest version of the software.
Method 1
Install VirtualBox from Ubuntu Repository
Open the terminal and run this command.
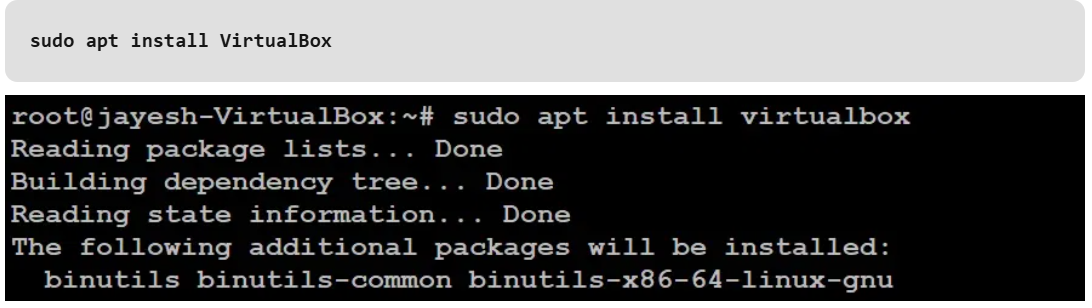
Verify Installation
We use the `dpkg` command, which is used to manage installed packages on Debian-based systems like Ubuntu.
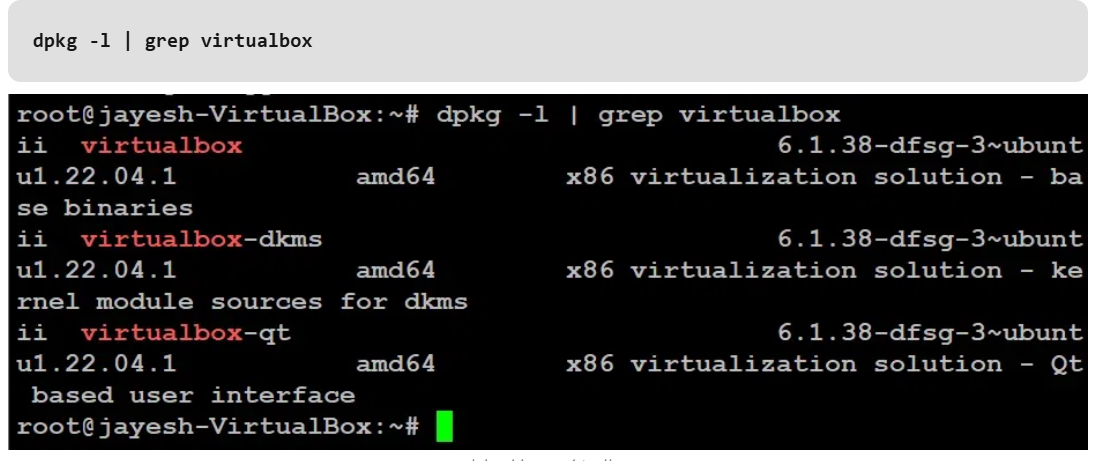
Method 2
Install VirtualBox using GUI (Graphical User Interface)
Step 1
Double Click on this
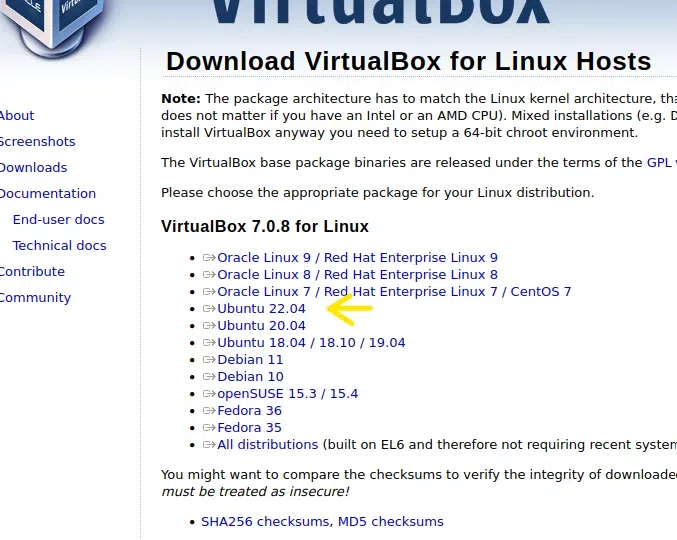
Step 2
Follow the numbering.
First Right click and select 'open with other application', then follow the numbering.
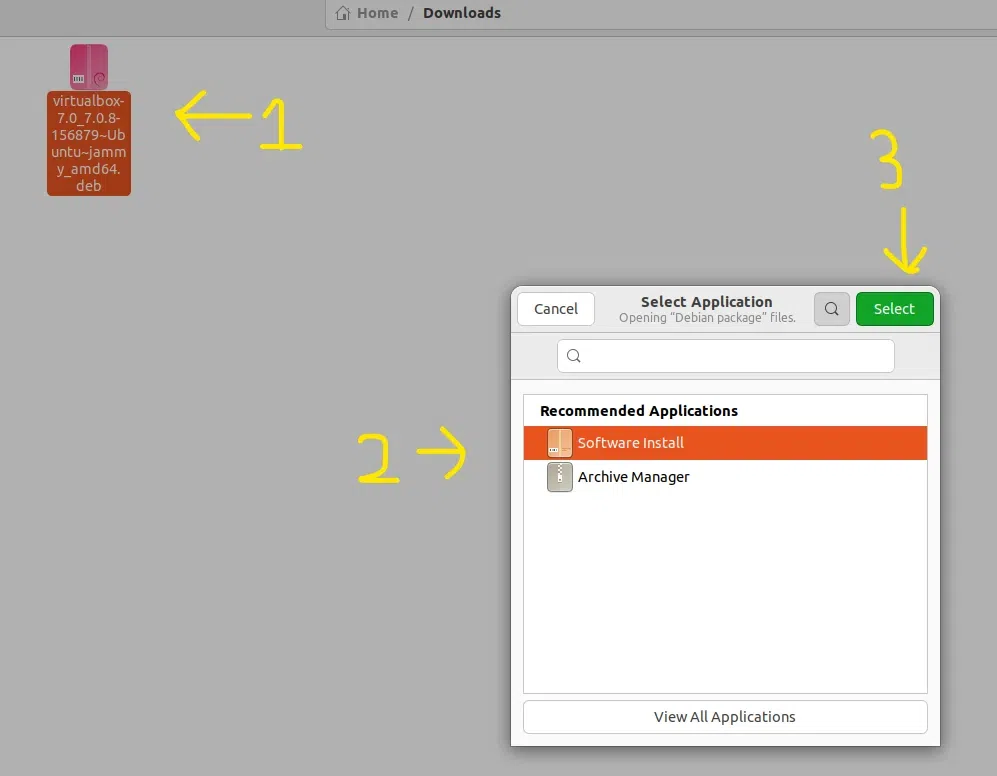
Step 3
Click on Install
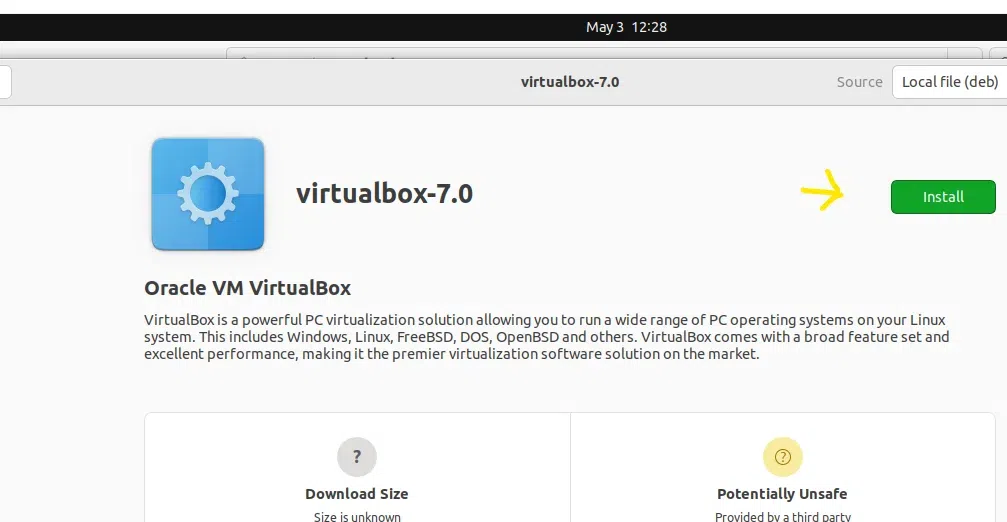
Step 4
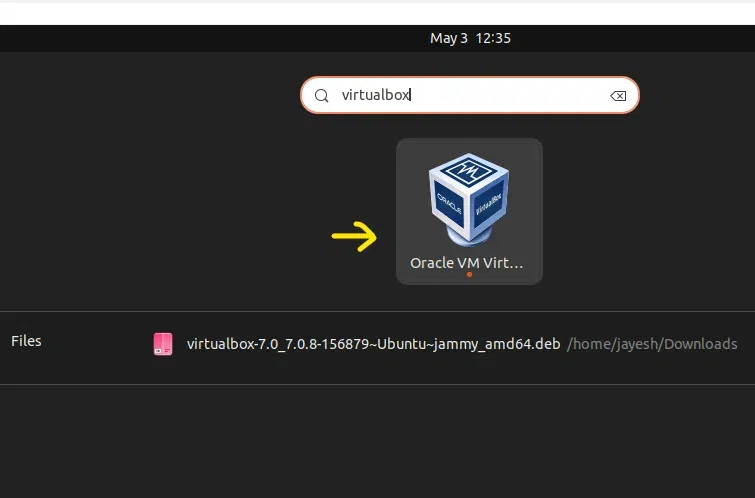
Search Virtualbox and Double click on application.
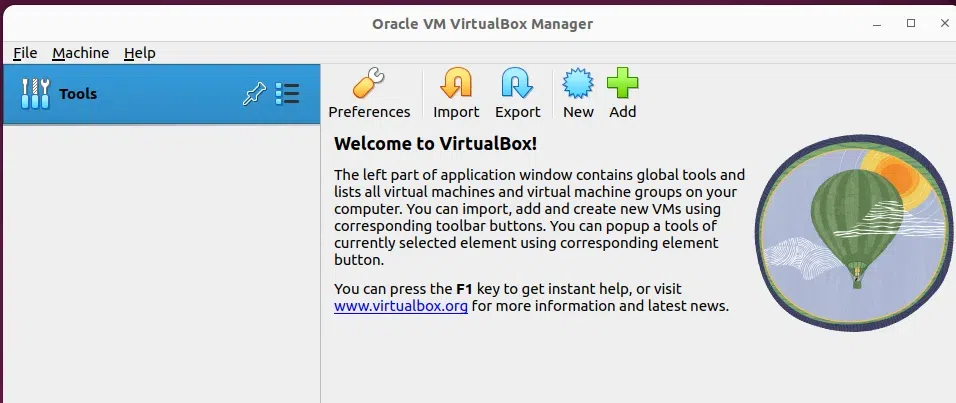
VirtualBox application Opened
Method 3
Installing VirtualBox using Oracle's repository
Step 1: Run this command in your terminal (adding key for the repository)

Step 2: Run this command in your terminal (adding Oracal VirtualBox repository in the repository list)

Step 3: Update the package list.

Step 4: Command for installation of virtualbox

Installing the Extension Pack
To unlock advanced features like USB 2.0/3.0 support, RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol), and PXE boot, you need to install the Extension Pack.
Steps:
Download the Extension Pack: Run the following command in the terminal:

This will enable support for extra features in VirtualBox, making it more powerful and flexible.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
1. Kernel Module Not Loading
If VirtualBox isn't starting properly, it could be because the kernel module isn’t loaded. To fix this, run the following command in the terminal:

This command rebuilds the VirtualBox kernel module.
2. "Virtualization Not Enabled" Error
If you see an error about virtualization not being enabled, it means your system’s BIOS/UEFI needs to have virtualization features turned on. To fix this:
- Restart your computer and enter the BIOS/UEFI settings.
- Look for a setting called Intel VT-x (or AMD-V for AMD processors).
- Enable it, save your settings, and restart.
3. Dependency Errors
Sometimes VirtualBox might fail to install due to missing dependencies. If you see errors like that, simply run

Conclusion
VirtualBox lets you run multiple operating systems on a single machine, ideal for testing, development, and learning. You can install it from the Ubuntu repository, GUI, or Oracle’s repository, each offering different advantages. Don't forget to install the Extension Pack for advanced features like USB and RDP support. If you run into issues, solutions for kernel modules, virtualization settings, and dependencies are easy to follow. VirtualBox provides the flexibility to create and configure virtual machines as needed for various tasks.